Show the code
Unbalanced panel data set with 1031 rows and the following time period frequencies: 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984
80 138 140 140 140 140 140 78 35 Linear dynamic panel data models account for dynamics and unobserved individual-specific heterogeneity. Due to the presence of lagged dependent variables, applying ordinary least squares including individual-specific dummy variables is inconsistent.
\[y_{it}=\alpha y_{i,t-1}+\beta x_{i,t}+u_{i,t}\] \[u_{i,t}=\eta_i+\varepsilon_{i,t}\] \[y_{it}=\alpha y_{i,t-1}+\beta x_{i,t}+\eta_i+\varepsilon_{i,t}\]
First Difference to elliminate \(\eta_i\)
\[\Delta y_{it}=\alpha \Delta y_{i,t-1}+\beta \Delta x_{i,t}+\Delta \varepsilon_{i,t}\]
n=140 firms T=9
Unbalanced panel data set with 1031 rows and the following time period frequencies: 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984
80 138 140 140 140 140 140 78 35 strucUPD.plot(dat,i.name = "firm",t.name = "year")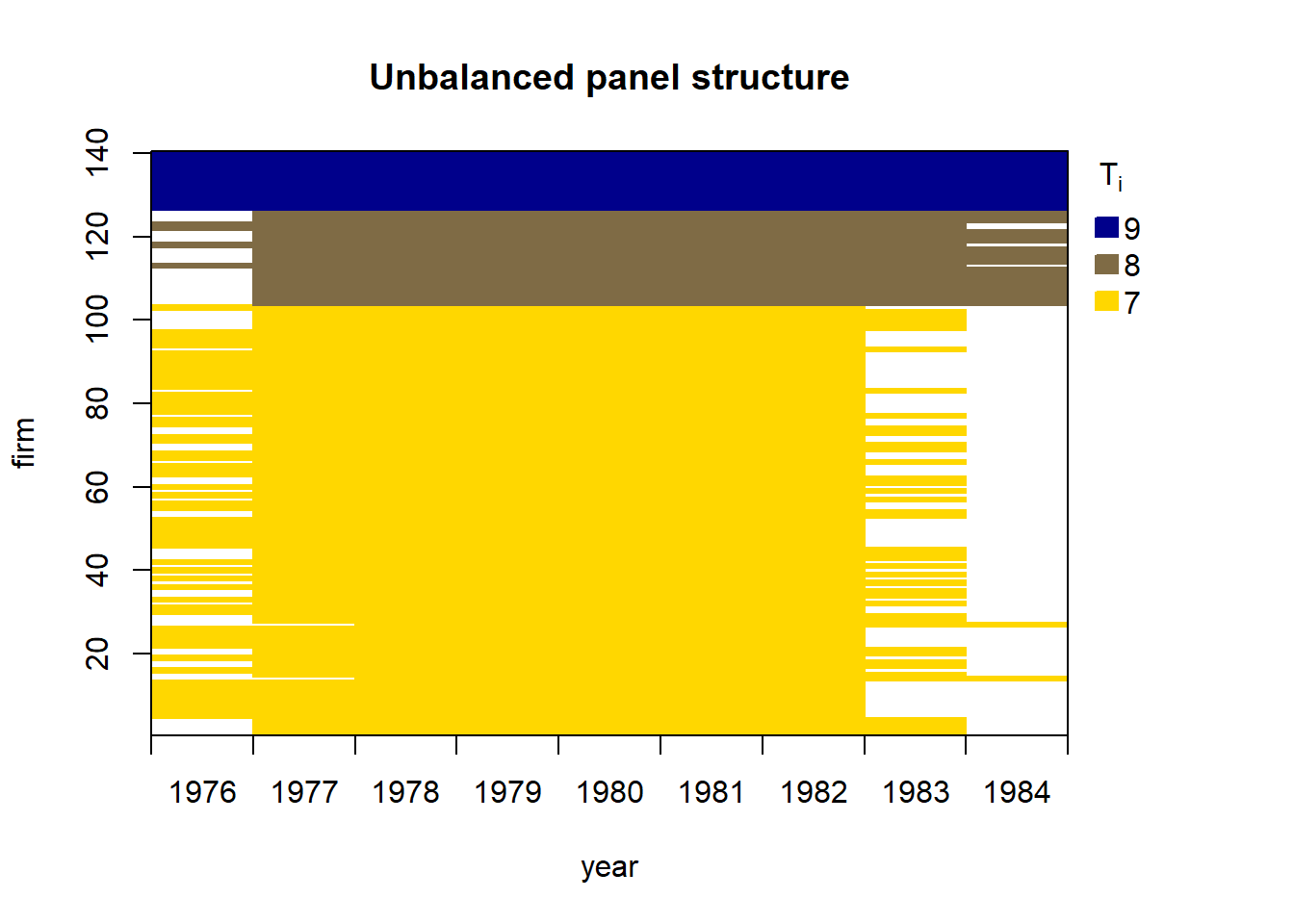
m1 <- pdynmc(
dat = dat,
varname.i = "firm",
varname.t = "year",
use.mc.diff = TRUE,
use.mc.lev = FALSE,
use.mc.nonlin = FALSE,
include.y = TRUE,
varname.y = "n",
lagTerms.y = 2,
fur.con = TRUE,
fur.con.diff = TRUE,
fur.con.lev = FALSE,
varname.reg.fur = c("w", "k", "ys"),
lagTerms.reg.fur = c(1,2,2),
include.dum = TRUE,
dum.diff = TRUE,
dum.lev = FALSE,
varname.dum = "year",
w.mat = "iid.err",
std.err = "corrected",
estimation = "twostep",
opt.meth = "none"
)
summary(m1)
Dynamic linear panel estimation (twostep)
GMM estimation steps: 2
Coefficients:
Estimate Std.Err.rob z-value.rob Pr(>|z.rob|)
L1.n 0.62871 0.19341 3.251 0.00115 **
L2.n -0.06519 0.04505 -1.447 0.14790
L0.w -0.52576 0.15461 -3.401 0.00067 ***
L1.w 0.31129 0.20300 1.533 0.12528
L0.k 0.27836 0.07280 3.824 0.00013 ***
L1.k 0.01410 0.09246 0.152 0.87919
L2.k -0.04025 0.04327 -0.930 0.35237
L0.ys 0.59192 0.17309 3.420 0.00063 ***
L1.ys -0.56599 0.26110 -2.168 0.03016 *
L2.ys 0.10054 0.16110 0.624 0.53263
1979 0.01122 0.01168 0.960 0.33706
1980 0.02307 0.02006 1.150 0.25014
1981 -0.02136 0.03324 -0.642 0.52087
1982 -0.03112 0.03397 -0.916 0.35967
1983 -0.01799 0.03693 -0.487 0.62626
1976 -0.02337 0.03661 -0.638 0.52347
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
41 total instruments are employed to estimate 16 parameters
27 linear (DIF)
8 further controls (DIF)
6 time dummies (DIF)
J-Test (overid restrictions): 31.38 with 25 DF, pvalue: 0.1767
F-Statistic (slope coeff): 269.16 with 10 DF, pvalue: <0.001
F-Statistic (time dummies): 15.43 with 6 DF, pvalue: 0.0172mtest.fct(m1,t.order = 2)
Arellano and Bond (1991) serial correlation test of degree 2
data: 2step GMM Estimation
normal = -0.36744, p-value = 0.7133
alternative hypothesis: serial correlation of order 2 in the error termsThe test does not reject the null hypothesis at any plausible significance level and provides no indication that the model specification might be inadequate.
jtest.fct(m1)
J-Test of Hansen
data: 2step GMM Estimation
chisq = 31.381, df = 25, p-value = 0.1767
alternative hypothesis: overidentifying restrictions invalidwald.fct(m1,param = "all")
Wald test
data: 2step GMM Estimation
chisq = 1104.7, df = 16, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: at least one time dummy and/or slope coefficient is not equal to zero